To complement our series of QuickReads covering measurement, we will now explore Failure Demand (FD).…

ChangeWise Guide to FMEA
In this guide, we offer a high-level overview of FMEA, including where it comes from, its key principles and why it’s effective in identifying potential failures in a system, along with their cause and effect.
What is FMEA?
FMEA stands for ‘Failure Mode Effects Analysis’. It is a systematic method for identifying, assessing and mitigating possible failures that pose the greatest risk to products and services. It can be used to evaluate both current and future processes, products and services.
Key Features
⭐️ Organises actual and possible process failures and their associated risks.
⭐️ Can be used anytime and asks: what can/does go wrong, how and why?
⭐️ Will uncover problems that may result in
- Defects or errors in a process delivering a product or service
- Reduced process efficiency
⭐️ From this information, action can be taken to reduce or eliminate risks
Where did the concept of FMEA originate?
FMEA was described in US Armed Forces Military Procedure documents in 1949 and by the early 1960s, NASA were applying variations of the method. During the 1970s, use of FMEA and related techniques spread to other industries, including automotive. Ford Motor Company introduced the methodology to improve safety and also applied the same approach to their processes (PFMEA), to consider potential process induced failures prior to launching production.
Today, FMEA methodology is used extensively in a variety of industries. At Changewise, we regularly introduce the methodology to a multitude of client sectors, all who find it beneficial in reducing and managing defects/risks.

Photo by Sarah Kilian on Unsplash
FMEA in more detail……
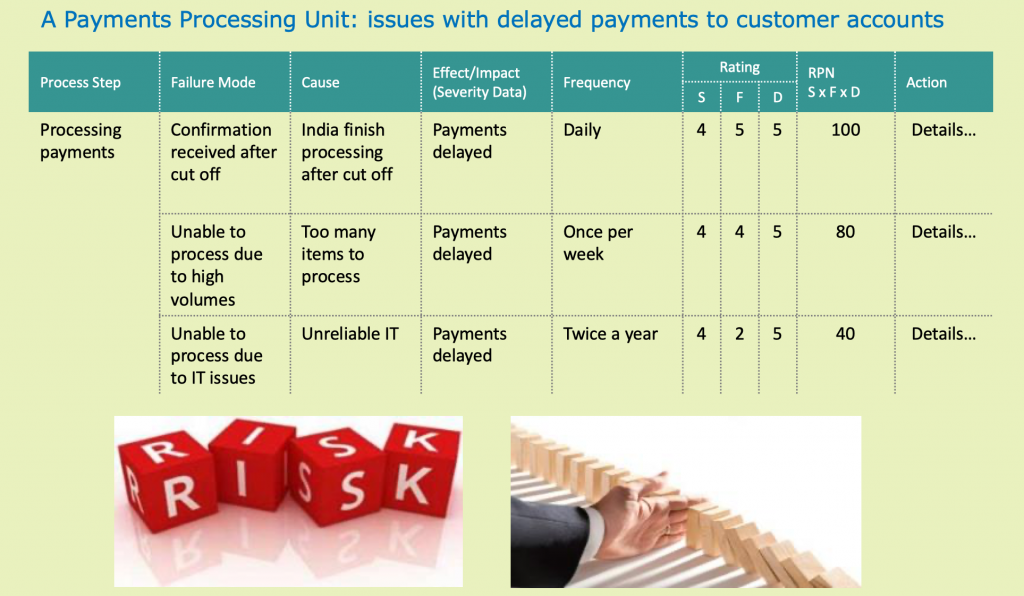
FMEA uses 5 simple steps. Let’s use a payment processing unit as an example to help us.
Step 1: Identify potential failures and their effect/impact
This involves completing some analysis to identify your risks (failure modes), their cause and resulting impact (effect).
For example:
Failure Mode: payment confirmation is received after processing cut-off time.
Cause: The team are offshore and their processing time is not in harmony with the customer needs/operating hours.
Effect/Impact: Payments are delayed.
Step 2: Understand the severity.
Once you have a list of failure modes, each item is assigned a rating from 1-5 based on the seriousness of the error consequence:
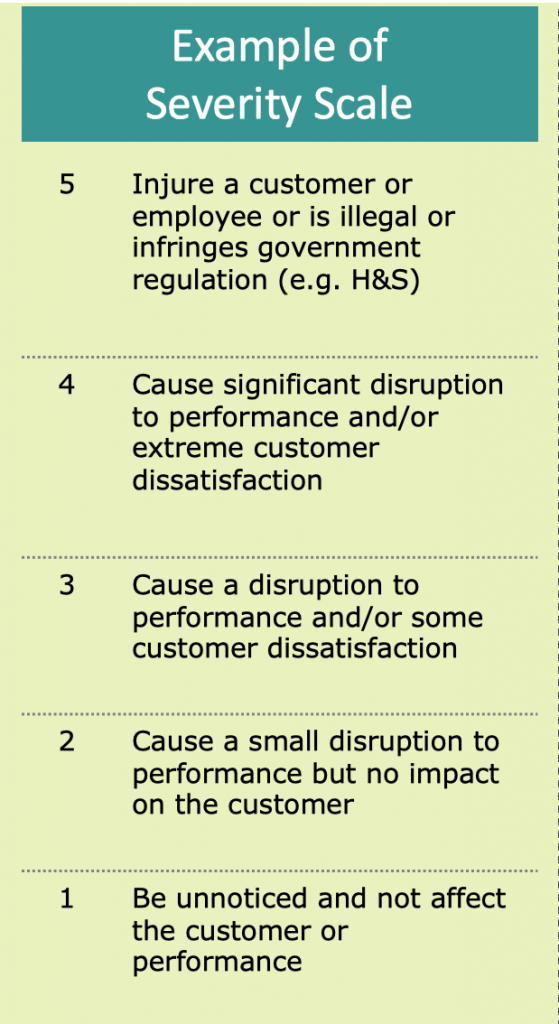
Example: Delaying payment would cause significant customer dissatisfaction, so our example would have a rating of S4.
Step 3: How often does the error occur?
Complete analysis to understand how frequently the failure mode occurs, and provide a frequency rating from 1-5:

Example: Our payment issue is happening daily, so a frequency rating of 5 is applied.
Step 4: Failure Mode Detection
How easy would it be to detect the failure in the current process? This provides you with a detection rating of 1 to 5. The higher the rating, the harder it is to identify the issue:

Example: There is no process for identifying the payment cut off failure mode and no control, so a rating of 5 is applied.
Step 5: Assign a Risk Priority Number (RPN)
After completing the above steps, each failure mode is assigned an RPN. This is a simple calculation:
RPN = Severity X Frequency X Detection (S x F x D)
Example: This gives our payment processing example an SFD rating of 100
Key Benefits
Once you have your full list of Failure Modes and their associated RPN’s, the FMEA can be used to assess and improve:
🙂 Which issues can be easily prevented
🙂 The impact of failure modes
🙂 The occurrence/frequency of failure modes
🙂 The strength of error detection rates

Photo by Rachael Gorjestani on Unsplash
In Summary
FMEA stands for ‘Failure Mode Effects Analysis’ and acts as a systematic method for identifying, assessing and mitigating possible failures that pose the greatest risk to products and services. FMEA organises actual and possible process failures using a simple 5-step process.
Want to know more? Get in touch with the ChangeWise team at info@changewise.co.uk
ChangeWise believes employee engagement is the foundation for successful Change. Training and coaching your people to use simple continuous improvement techniques will enable your organisation to continuously adapt and stay ahead in a constantly changing and challenging environment.
For updates and interesting Lean Change insights, connect with us on LinkedIn.



